Biomass power generation is attracting attention as a clean energy that can reduce the carbon dioxide emission coefficient and is also a stable method of power generation.
We design plants that generate renewable and friendly energy for the future of the planet.
GNPW Group | biomass
How does biomass work?
Biomass is any organic matter that can be transformed into energy, whether electrical, thermal or even mechanical.
And its origin is very diverse and can be wood, sugar cane, soy, rice, urban and industrial waste.
The large-scale production of electricity from agricultural biomass is related to the use of efficient technologies and a strong agroindustry with large plantations, whether soybean, rice, corn or sugar cane.
In this way, biomass is obtained from the processing of residues from the cultures mentioned above, such as corn, where it is possible to use cob, stalk, leaf and straw as raw material. From soy and rice, the residues that remain in the field, and are treated like straw.
In this way, biomass is obtained from the processing of residues from the cultures mentioned above, such as corn, where it is possible to use cob, stalk, leaf and straw as raw material. From soy and rice, the residues that remain in the field, and are treated like straw.
And from sugar cane, bagasse, straw and vinasse.
According to a study by the Statistical Review of World Energy, published in June 2008 by BP Global (Beyhond Petroleum, the new name of British Petroleum) the estimated amount of existing biomass on Earth is around 1.8 trillion tons.
This volume, when confronted with the degree of efficiency of the plants operating in the world in 2005, points to a generation capacity of 11 thousand TWh per year in the long term – or more than half of the total electricity produced in 2007, which was 19.89 thousand TWh.
According to a study by the Statistical Review of World Energy, published in June 2008 by BP Global (Beyhond Petroleum, the new name of British Petroleum) the estimated amount of existing biomass on Earth is around 1.8 trillion tons.
This volume, when confronted with the degree of efficiency of the plants operating in the world in 2005, points to a generation capacity of 11 thousand TWh per year in the long term – or more than half of the total electricity produced in 2007, which was 19.89 thousand TWh.
The GNPW Group has the expertise to develop projects for the production of electricity from biomass according to market demand.
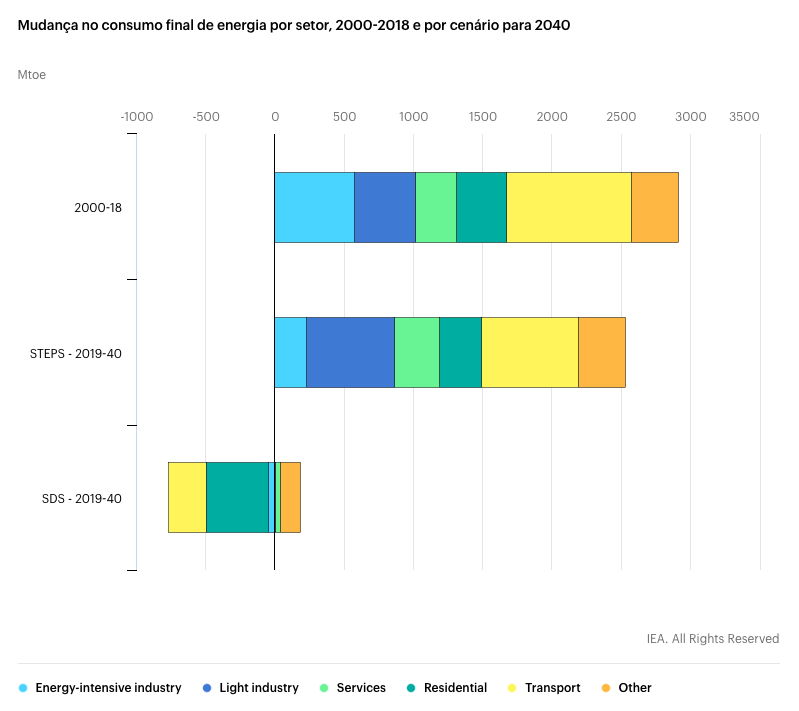
The global energy consumption
increased by 2.9% in 2018
The growth was the strongest since 2010 and nearly double the 10-year average. Demand for all fuels increased and renewables took second place with an 18% increase.
Biomass as a source of electrical energy has grown in Brazil, mainly in cogeneration systems (where it is possible to obtain thermal and electrical energy) in the industrial and service sectors. Sugarcane is a resource with great potential, and its participation is important not only for the diversification of the electricity matrix, but also because the harvest coincides with the dry period in the Southeast/Center-West region, where sugarcane is concentrated. highest installed capacity in hydroelectric dams in the country. The electricity supplied during this period helps, therefore, to preserve the levels of the UHEs' reservoirs.
(Source: ANEEL)
(Source: ANEEL)
It is estimated that for the next few years the electricity produced by the sector will represent 15% of the Brazilian matrix
With the production of 14,400 average MW.
Benefits:
Abundance of biomass
in Brazil;
in Brazil;
Simpler environmental licensing;
They can be close to large urban centers;
Reduction of CO2 emissions;
Reduction in transmission cost.
The Southeast region has the greatest potential for electricity production:
1º State of São Paulo with 609.4 million gigajoules (GJ) per year;
2º Paraná with 65.4 million GJ annually;
3º Minas Gerais with 63.2 million GJ annually.
Projections of the International Energy Agency (1998) indicate that the world generation of electricity through Biomass
It should go from 10 TWh in 1995 to 27 TWh in 2020 (AEI, 1998).
Biomass plants complement the Hydroelectric Generation park, since the predominance of hydraulic power in the Brazilian electrical system causes the price of energy to be influenced by the flows of the rivers that have hydroelectric plants. In this way, the existence of an offer with a low cost of operation, mainly that can generate electricity in times of lower water availability, helps to mitigate the effects of lower relative storage.